STRADDLING THE WHITTIER FAULT - For those who come across this online publication that occasionally publishes articles (and should do so more often) about Southern California you know we are very fascinated by the mystery of earthquakes. As much as some of us try to pretend otherwise, earthquakes are apart of the fabric of life in Southern California as Sig-Alerts, high-rent, Disneyland and the ocean. In fact, if you are stuck in the middle of a Sig-Alert right now you may be sitting on top of an earthquake fault-line (like the Whittier Fault that cuts across The Orange Freeway above Brea).
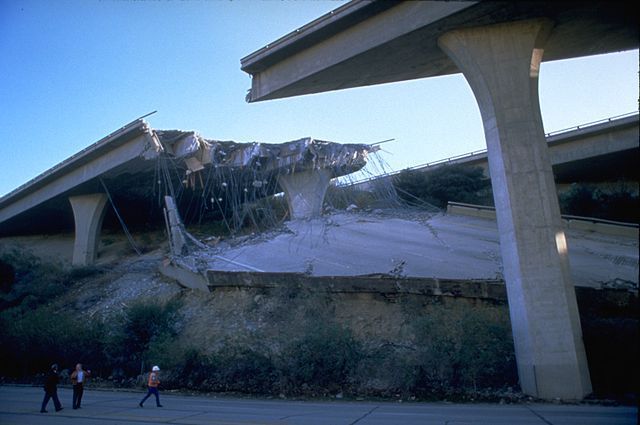

Major damage to Interstate 5 at Gavin Canyon near the Santa Clarita Valley following the 1994 Northridge Earthquake. Photograph by FEMA and in public domain.
Since the aftermath of the 1994 Northridge Earthquake it has been noted by more than a few people, over at the United States Geological Survey and elsewhere, that things have been a little too quiet. In the last couple years have there been regular, noticeable jolts in the Los Angeles basin. In the past few weeks there have been a few magnitude 3 earthquakes along the Newport-Inglewood Fault, and there has also been some minor shaking going on out in the Inland Empire. That, along with the recent Nepal Earthquake, which is about the size we expect "The Big One" here in Southern California to be, has quite a few people talking, and hopefully they are preparing for next big quake.
In previous posts here we have talked about myths, facts and figures about Southern California earthquakes, but let us give a thought to other forms of earthquake preparedness.
There is a lot written elsewhere about earthquake preparedness and please, please, please take the time to read the information and prepare. Here, we want to present some advice and information that sometimes gets lost in earthquake preparedness.
Much is written about what to do at home or work when Mother Nature starts quaking, but in preparing for "The Big One," or a big enough one, here are some other things to consider when you are preparing.
Getting BACK Home From Work
Much is talked about what to do in the workplace during and after an earthquake, and perhaps your place of business has an emergency plan, but what about getting home after a major earthquake. As plenty of you know commuting to work from, say, San Bernardino to Downtown L.A., is the norm in our part of the world. So, what happens if a big enough earthquake strikes in the middle of the afternoon causing major damage to The San Bernardino, Pomona and Foothill Freeways? How will you get back home? After all, think of those times when there is a major accident, a Sig-Alert, closing a freeway and how badly that backs up traffic, and the ripple affect across the entire freeway system.
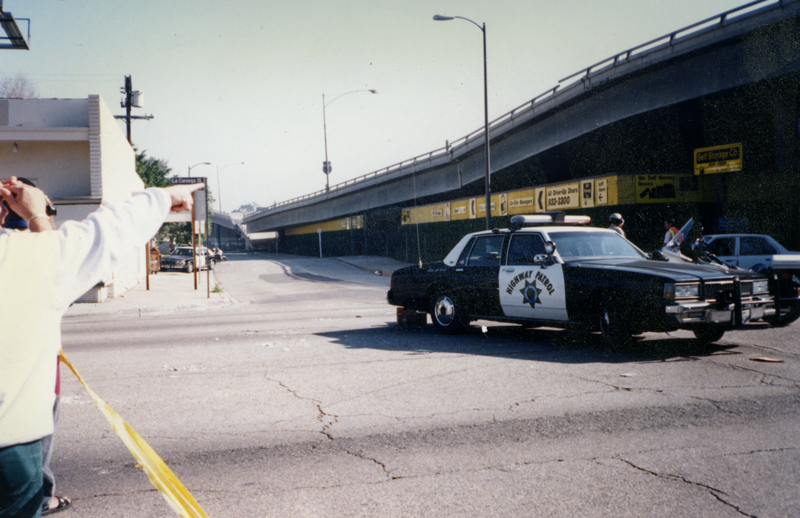

Collapsed portion of The Santa Monica Freeway at La Cienega Blvd. Used under a Creative Commons license.
For commuters who use public transit, and for those drivers looking at public transit to get back home, it is likely Metrolink, along with the Metro light rail routes and subway, will be shut down for a time so the tracks can be inspected.
So, whether you commute from the Inland Empire to L.A., L.A. to Orange County, or Orange County to the Inland Empire (you get the idea), it is very important to think how you will get back home if there is freeway damage, along with other possible severe damage that could make it near impossible to drive back home right away.
Just as well, what if your car is damaged in the earthquake? What do you do then?
This is why it is extremely important to have an earthquake preparedness kit at work and/or in your car. Even if you live very close to where you work it is important to have a plan how to get back home.
Chances are after a major earthquake you are probably going to want to get in your car and get home to make sure everything is okay, and understandably so. However, it is best to stay where you are at for a time (if it is structurally safe, or go to an open, safe space) listen to the radio, or television if one is available, or gather information online if you can get Internet service, and get information about the earthquake. Once you understand the scope of the earthquake you can begin to plan how to get back home. There may be more of an urgency, and down right understandable panic, if you learn the epicenter is at or near where you live. Again, even if the news reports from where you live sound ominous, you must keep your safety in mind.
Depending on how severe the earthquake is it certainly is possible you may have to spend the night at the office, or you can maybe spend the night at a co-worker's home, or maybe a hotel/motel, if they are not already filled, or damaged. You may have to consider spending the night in your car.
You must also remember, power will likely be out and places where you could buy food and other such things will likely be closed or just simply inoperable. (If the goodwill of people and businesses of past disasters in America are any indication of what to expect it is possible such businesses may just handout food to those stranded, but do not count on it.)
Now, if you live close, or close enough, to work, and there is serve damage you may consider walking home.
So, with Southern California's infamously long commutes you need to think and plan how you will get home following a major earthquake.
There Is Freeway Damage. So, I'll Just Take the Side-Streets
Okay, so you have heard and seen major freeway damage, and so you may think, why not just take the side-streets back home. While a lot of people may think they can take side-streets to get back home you must keep in mind there could be a lot of obstacles in the aftermath of a major earthquake that could make driving side-streets dangerous.
The most obvious will be the power-outage affecting traffic signals, backing up traffic. Furthermore, the streets may have larges cracks in them; power-lines could be down on the streets; shattered glass and other debris may be in the streets; busted water pipes could flood the street; natural gas lines may be broken; and aftershocks could cause further damage.
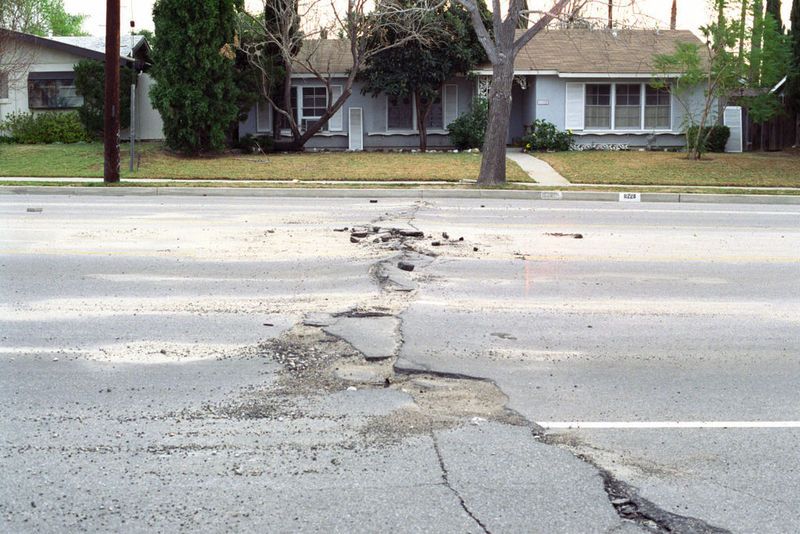

Street Damage in the San Fernando Valley following the 1994 Northridge Earthquake. Used under a Creative Commons license.
This is why it is important to try to be calm at work and hang back at work after the shock, or where ever you may be in the middle of the day, and try to get as much information as possible about the earthquake before making a decision to drive back home.
Most news media, working along with the California Highway Patrol, Metro and other authorities, will try to get you the best information in taking alternative routes back home.
If it is safe to drive back home be prepared to spend several hours in traffic, as those commuters in the 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake can attest to. Also, make sure there is gas in your car's gas tank. With power-outages and other possible damage many gas stations will likely be closed.
"DID YOU FEEL IT!?"
Even in small earthquakes a lot of people just have the call and/or text asking that question, "Did you feel it?" Chances are if it is a big enough earthquake they probably did.
Emergency planners often said back in the 1980s and 1990s, "Don't use the telephone after a big earthquake unless it's for an emergency." That remains true today, and since you likely want to contact somebody important to you after a big enough earthquake text messaging is the way to go. Communicating by text message will not use much data as opposed to making an actual telephone call, and thus will free telephone lines for emergency and important calls. As much as you may want to contact "everybody" after a major earthquake you should just send text messages to those important to you as even text messages can overload the system.
It is important to remember if there is a massive power-outage following an earthquake, and/or the cell-phone towers are damaged, you may be without telephone and data service. If you really need to get a-hold of somebody you may have to find and kindly ask to use somebody's landline telephone, or find one of those fading relics from the past, a payphone.
Even when cell-phone service does come back coverage may be spotty or non-existent at times.
Since so many people these days, both at home and work, only have cell/smartphones the city of L.A. recently introduced legislation to retrofit cell-phone towers. This legislation is the first of its kind in the nation.
When To Call 911 or Other Authorities
Even in small earthquakes 911 centers quickly fill with calls. Most, if not all in those calls, are frivolous and tie up the emergency lines. Even in major earthquakes 911 dispatchers are inundated with frivolous calls. In fact, dig around YouTube and you will find audio of such calls following a major earthquake.
Always call 911 if it is a life-threatening emergency. Do not call 911 to ask for information or ask about rumors. It is also best NOT to call 911 if windows on a building are shattered and nobody is hurt. Of course, and please, do check and see to make sure everybody in the home and/or business where the shattered windows occurred are okay. There have been many cases where the 911 system is tied up by people reporting broken windows, but nobody is hurt.
If there is a fire, collapsed building, collapsed freeway, or something that looks to be a threat to public safety and there are no emergency workers on the scene that is when it is best to call 911. When you must call 911 try to give as much detailed information as possible.
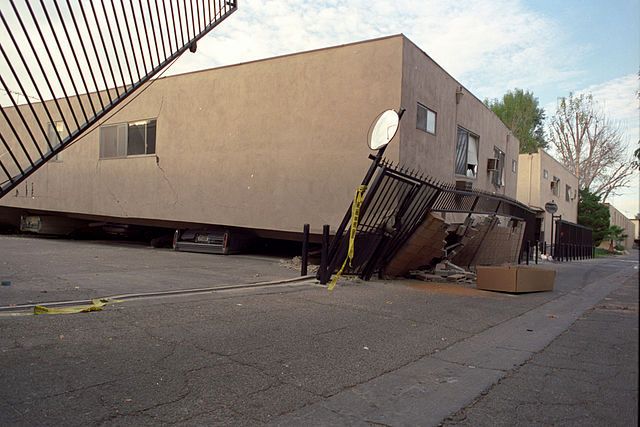

Collapsed apartment building following the 1994 earthquake. Used under a Creative Commons license.
A note about calling the non-emergency dispatch line for certain kinds of information. Before calling a police or fire non-emergency dispatch number make sure the information you seek is already available in the media or social media. Non-emergency dispatchers will likely be doing double duty as 911 dispatchers.
Where Are The Emergency Responders?
If you call 911 for an emergency you may hear the dispatcher say, "We'll get somebody out there as soon as we can," and soon discover it is taking quite awhile for emergency responders to arrive. Emergency planners and organizations across Southern California have stressed that in the aftermath of a major earthquake emergency responders are not going to be able to get to every emergency right away. For many years we have been used to, and down right accustomed to, emergency responders arriving quickly during major emergencies, like brush fires. In the aftermath of a major earthquake it may take awhile for emergency responders to respond to a major emergency.
How You Can Help
This is where you can help. Well before the big quake you should consider participating in your local Community Emergency Response Team (CERT). CERT, according to FEMA, "educates people about disaster preparedness for hazards that may impact their area and trains them in basic disaster response skills, such as fire safety, light search and rescue, team organization, and disaster medical operations."
In the immediate aftermath of a major earthquake this is one way you can help your community, and how you can slowly rebuild and try to get things back to normal in your neighborhood.
Don't Forget The Toilet!
As the 2014 La Habra Earthquake showed, it does not take much big shaking for water pipes to be shaken loose and burst. Even when the ground is stable it seems pipes easily burst, as evident of pipes bursting around L.A. in the past several years. A lot of pipes are expected to burst during the next big earthquake, and that may leave you without plumbing, and thus no toilet to flush. So, what can you do to prepare if your plumbing breaks during an earthquake?
Put some plastic trash bags aside in your emergency preparedness kit, and use those.
How to use plastic bags as makeshift toilets? Line the plastic bag along the toilet seat, kind of like you do with the trash can, and there you have a makeshift toilet, which you can later, when needed, move the waste into the trash can.
Social Media
During major news events social media has played an extraordinarily important role in getting information out to people from officials very quickly. At the same time, during major news events, a lot of misinformation has been quickly spread on social media. Most of the time this is information is quickly corrected by officials and/or news media. Of course, there are people on social media who pass false information for the sake of simply doing so, and, on Twitter, it gets retweeted dozens of times. In the aftermath of a major quake such false reports could quickly spread undue panic in an already tense situation (false social media reports have already done just that in past disasters).
If somebody on social media is claiming something major is happening, like, for example, a freeway has collapsed or lots of fires are burning, instead of retweeting it try to send that information to the fire or police/sheriff's department and news media's social media account to see if they can verify it. The bottom line, make sure the information you are reading on social media is correct before sharing it.
This is all assuming you can get back on the Internet after a major earthquake. "The Big One" may very well cause major Internet disruptions that will be a real shock for a lot of people accustomed to always having the Internet available at their fingertips.
Check Your Insurance
Before the next big earthquake, or other disaster, now is the time to check your insurance policy to make sure and confirm what covers what when all goes wrong.
It is very important to understand earthquake insurance is only offered through a state agency, the California Earthquake Authority, and flood insurance is offered through the federal government.
Unfortunately, in the aftermath of disasters we read way too many stories in the news how insurance will not cover certain things for a certain reason.
Earlier we mentioned about your car being possibly damaged in an earthquake. See if an earthquake damaged car is covered by your auto insurance. Some auto insurance companies have "Acts of God" clauses in them, which may, or may not, cover your vehicle should it be damaged or destroyed in an earthquake.
It may be a complicated pain to deal with insurance organizations and their tons of paperwork in that sometimes complicated legal language, but now is the time to go over your policy. Furthermore, now is the time to think, talk over and decide if you need different insurance coverage.
Getting Back To Work
At the top of this list we talked about what plans you should make getting back home from work following a big earthquake. As the aftershocks diminish life will slowly get back to normal, and part of that is getting back to work, but with collapsed freeways that may prove tricky.
Those who remember the 1994 earthquake remember some very long commutes. Even though there was an urgent surge in retrofitting freeways following the 1989 Loma Prieta and 1994 Northridge Earthquakes, in the next major earthquake Southern California emergency planners expect some major freeway damage.
If the Internet is back up and operating as normal you may be able to work from home, depending on what you do. However, if you have to make the commute, well, you may want to think about public transit.
The then fledgling Metrolink received a big, unexpected boost following the 1994 earthquake, and expanded well ahead of schedule.
Now if your place of employment was damaged or destroyed in the earthquake you may have Disaster Unemployment Assistance available to you through the state's Employment Development Department.
The Bottom Line
The bottom line is this, the next major earthquake is going to cause a serious or outright major disruption for us, and it may very well change our way of life for a time (just think, the Internet may not be available at your fingertips). However, do understand, and it sounds like a cliché, the better we prepare, the better we will get through this.

Major damage to Interstate 5 at Gavin Canyon near the Santa Clarita Valley following the 1994 Northridge Earthquake. Photograph by FEMA and in public domain.
Since the aftermath of the 1994 Northridge Earthquake it has been noted by more than a few people, over at the United States Geological Survey and elsewhere, that things have been a little too quiet. In the last couple years have there been regular, noticeable jolts in the Los Angeles basin. In the past few weeks there have been a few magnitude 3 earthquakes along the Newport-Inglewood Fault, and there has also been some minor shaking going on out in the Inland Empire. That, along with the recent Nepal Earthquake, which is about the size we expect "The Big One" here in Southern California to be, has quite a few people talking, and hopefully they are preparing for next big quake.
In previous posts here we have talked about myths, facts and figures about Southern California earthquakes, but let us give a thought to other forms of earthquake preparedness.
There is a lot written elsewhere about earthquake preparedness and please, please, please take the time to read the information and prepare. Here, we want to present some advice and information that sometimes gets lost in earthquake preparedness.
Much is written about what to do at home or work when Mother Nature starts quaking, but in preparing for "The Big One," or a big enough one, here are some other things to consider when you are preparing.
Getting BACK Home From Work
Much is talked about what to do in the workplace during and after an earthquake, and perhaps your place of business has an emergency plan, but what about getting home after a major earthquake. As plenty of you know commuting to work from, say, San Bernardino to Downtown L.A., is the norm in our part of the world. So, what happens if a big enough earthquake strikes in the middle of the afternoon causing major damage to The San Bernardino, Pomona and Foothill Freeways? How will you get back home? After all, think of those times when there is a major accident, a Sig-Alert, closing a freeway and how badly that backs up traffic, and the ripple affect across the entire freeway system.

Collapsed portion of The Santa Monica Freeway at La Cienega Blvd. Used under a Creative Commons license.
For commuters who use public transit, and for those drivers looking at public transit to get back home, it is likely Metrolink, along with the Metro light rail routes and subway, will be shut down for a time so the tracks can be inspected.
So, whether you commute from the Inland Empire to L.A., L.A. to Orange County, or Orange County to the Inland Empire (you get the idea), it is very important to think how you will get back home if there is freeway damage, along with other possible severe damage that could make it near impossible to drive back home right away.
Just as well, what if your car is damaged in the earthquake? What do you do then?
This is why it is extremely important to have an earthquake preparedness kit at work and/or in your car. Even if you live very close to where you work it is important to have a plan how to get back home.
Chances are after a major earthquake you are probably going to want to get in your car and get home to make sure everything is okay, and understandably so. However, it is best to stay where you are at for a time (if it is structurally safe, or go to an open, safe space) listen to the radio, or television if one is available, or gather information online if you can get Internet service, and get information about the earthquake. Once you understand the scope of the earthquake you can begin to plan how to get back home. There may be more of an urgency, and down right understandable panic, if you learn the epicenter is at or near where you live. Again, even if the news reports from where you live sound ominous, you must keep your safety in mind.
Depending on how severe the earthquake is it certainly is possible you may have to spend the night at the office, or you can maybe spend the night at a co-worker's home, or maybe a hotel/motel, if they are not already filled, or damaged. You may have to consider spending the night in your car.
You must also remember, power will likely be out and places where you could buy food and other such things will likely be closed or just simply inoperable. (If the goodwill of people and businesses of past disasters in America are any indication of what to expect it is possible such businesses may just handout food to those stranded, but do not count on it.)
Now, if you live close, or close enough, to work, and there is serve damage you may consider walking home.
So, with Southern California's infamously long commutes you need to think and plan how you will get home following a major earthquake.
There Is Freeway Damage. So, I'll Just Take the Side-Streets
Okay, so you have heard and seen major freeway damage, and so you may think, why not just take the side-streets back home. While a lot of people may think they can take side-streets to get back home you must keep in mind there could be a lot of obstacles in the aftermath of a major earthquake that could make driving side-streets dangerous.
The most obvious will be the power-outage affecting traffic signals, backing up traffic. Furthermore, the streets may have larges cracks in them; power-lines could be down on the streets; shattered glass and other debris may be in the streets; busted water pipes could flood the street; natural gas lines may be broken; and aftershocks could cause further damage.

Street Damage in the San Fernando Valley following the 1994 Northridge Earthquake. Used under a Creative Commons license.
This is why it is important to try to be calm at work and hang back at work after the shock, or where ever you may be in the middle of the day, and try to get as much information as possible about the earthquake before making a decision to drive back home.
Most news media, working along with the California Highway Patrol, Metro and other authorities, will try to get you the best information in taking alternative routes back home.
If it is safe to drive back home be prepared to spend several hours in traffic, as those commuters in the 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake can attest to. Also, make sure there is gas in your car's gas tank. With power-outages and other possible damage many gas stations will likely be closed.
"DID YOU FEEL IT!?"
Even in small earthquakes a lot of people just have the call and/or text asking that question, "Did you feel it?" Chances are if it is a big enough earthquake they probably did.
Emergency planners often said back in the 1980s and 1990s, "Don't use the telephone after a big earthquake unless it's for an emergency." That remains true today, and since you likely want to contact somebody important to you after a big enough earthquake text messaging is the way to go. Communicating by text message will not use much data as opposed to making an actual telephone call, and thus will free telephone lines for emergency and important calls. As much as you may want to contact "everybody" after a major earthquake you should just send text messages to those important to you as even text messages can overload the system.
It is important to remember if there is a massive power-outage following an earthquake, and/or the cell-phone towers are damaged, you may be without telephone and data service. If you really need to get a-hold of somebody you may have to find and kindly ask to use somebody's landline telephone, or find one of those fading relics from the past, a payphone.
Even when cell-phone service does come back coverage may be spotty or non-existent at times.
Since so many people these days, both at home and work, only have cell/smartphones the city of L.A. recently introduced legislation to retrofit cell-phone towers. This legislation is the first of its kind in the nation.
When To Call 911 or Other Authorities
Even in small earthquakes 911 centers quickly fill with calls. Most, if not all in those calls, are frivolous and tie up the emergency lines. Even in major earthquakes 911 dispatchers are inundated with frivolous calls. In fact, dig around YouTube and you will find audio of such calls following a major earthquake.
Always call 911 if it is a life-threatening emergency. Do not call 911 to ask for information or ask about rumors. It is also best NOT to call 911 if windows on a building are shattered and nobody is hurt. Of course, and please, do check and see to make sure everybody in the home and/or business where the shattered windows occurred are okay. There have been many cases where the 911 system is tied up by people reporting broken windows, but nobody is hurt.
If there is a fire, collapsed building, collapsed freeway, or something that looks to be a threat to public safety and there are no emergency workers on the scene that is when it is best to call 911. When you must call 911 try to give as much detailed information as possible.

Collapsed apartment building following the 1994 earthquake. Used under a Creative Commons license.
A note about calling the non-emergency dispatch line for certain kinds of information. Before calling a police or fire non-emergency dispatch number make sure the information you seek is already available in the media or social media. Non-emergency dispatchers will likely be doing double duty as 911 dispatchers.
Where Are The Emergency Responders?
If you call 911 for an emergency you may hear the dispatcher say, "We'll get somebody out there as soon as we can," and soon discover it is taking quite awhile for emergency responders to arrive. Emergency planners and organizations across Southern California have stressed that in the aftermath of a major earthquake emergency responders are not going to be able to get to every emergency right away. For many years we have been used to, and down right accustomed to, emergency responders arriving quickly during major emergencies, like brush fires. In the aftermath of a major earthquake it may take awhile for emergency responders to respond to a major emergency.
How You Can Help
This is where you can help. Well before the big quake you should consider participating in your local Community Emergency Response Team (CERT). CERT, according to FEMA, "educates people about disaster preparedness for hazards that may impact their area and trains them in basic disaster response skills, such as fire safety, light search and rescue, team organization, and disaster medical operations."
In the immediate aftermath of a major earthquake this is one way you can help your community, and how you can slowly rebuild and try to get things back to normal in your neighborhood.
Don't Forget The Toilet!
As the 2014 La Habra Earthquake showed, it does not take much big shaking for water pipes to be shaken loose and burst. Even when the ground is stable it seems pipes easily burst, as evident of pipes bursting around L.A. in the past several years. A lot of pipes are expected to burst during the next big earthquake, and that may leave you without plumbing, and thus no toilet to flush. So, what can you do to prepare if your plumbing breaks during an earthquake?
Put some plastic trash bags aside in your emergency preparedness kit, and use those.
How to use plastic bags as makeshift toilets? Line the plastic bag along the toilet seat, kind of like you do with the trash can, and there you have a makeshift toilet, which you can later, when needed, move the waste into the trash can.
Social Media
During major news events social media has played an extraordinarily important role in getting information out to people from officials very quickly. At the same time, during major news events, a lot of misinformation has been quickly spread on social media. Most of the time this is information is quickly corrected by officials and/or news media. Of course, there are people on social media who pass false information for the sake of simply doing so, and, on Twitter, it gets retweeted dozens of times. In the aftermath of a major quake such false reports could quickly spread undue panic in an already tense situation (false social media reports have already done just that in past disasters).
If somebody on social media is claiming something major is happening, like, for example, a freeway has collapsed or lots of fires are burning, instead of retweeting it try to send that information to the fire or police/sheriff's department and news media's social media account to see if they can verify it. The bottom line, make sure the information you are reading on social media is correct before sharing it.
This is all assuming you can get back on the Internet after a major earthquake. "The Big One" may very well cause major Internet disruptions that will be a real shock for a lot of people accustomed to always having the Internet available at their fingertips.
Check Your Insurance
Before the next big earthquake, or other disaster, now is the time to check your insurance policy to make sure and confirm what covers what when all goes wrong.
It is very important to understand earthquake insurance is only offered through a state agency, the California Earthquake Authority, and flood insurance is offered through the federal government.
Unfortunately, in the aftermath of disasters we read way too many stories in the news how insurance will not cover certain things for a certain reason.
Earlier we mentioned about your car being possibly damaged in an earthquake. See if an earthquake damaged car is covered by your auto insurance. Some auto insurance companies have "Acts of God" clauses in them, which may, or may not, cover your vehicle should it be damaged or destroyed in an earthquake.
It may be a complicated pain to deal with insurance organizations and their tons of paperwork in that sometimes complicated legal language, but now is the time to go over your policy. Furthermore, now is the time to think, talk over and decide if you need different insurance coverage.
Getting Back To Work
At the top of this list we talked about what plans you should make getting back home from work following a big earthquake. As the aftershocks diminish life will slowly get back to normal, and part of that is getting back to work, but with collapsed freeways that may prove tricky.
Those who remember the 1994 earthquake remember some very long commutes. Even though there was an urgent surge in retrofitting freeways following the 1989 Loma Prieta and 1994 Northridge Earthquakes, in the next major earthquake Southern California emergency planners expect some major freeway damage.
If the Internet is back up and operating as normal you may be able to work from home, depending on what you do. However, if you have to make the commute, well, you may want to think about public transit.
The then fledgling Metrolink received a big, unexpected boost following the 1994 earthquake, and expanded well ahead of schedule.
Now if your place of employment was damaged or destroyed in the earthquake you may have Disaster Unemployment Assistance available to you through the state's Employment Development Department.
The Bottom Line
The bottom line is this, the next major earthquake is going to cause a serious or outright major disruption for us, and it may very well change our way of life for a time (just think, the Internet may not be available at your fingertips). However, do understand, and it sounds like a cliché, the better we prepare, the better we will get through this.